Becoming a Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) is an excellent way to level up your cybersecurity career, but earning this prestigious certification requires rigorous preparation.
A crucial initial step is understanding the CISSP exam objectives, encompassing the 8 domains of the CISSP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK). Delving deeply into these domains requires significant time and effort. If you're uncertain about committing to the exam, it might seem impractical to invest so much upfront.
But don’t fret. We’re here to help. This article will explain each of the ISC2 CISSP domains, helping you understand the coverage of the certification and determine if you're ready to pursue it. We will also discuss the CISSP outline so you know what to expect in the examinations.
Let’s get started!
What is ISC2 CISSP CBK?
The CBK forms the foundation for the CISSP certification and is created and maintained by the International Information System Security Certification Consortium ISC2. This peer-developed compendium represents the expansive knowledge every CISSP aspirant must master.
Acting as a collection of global best practices in information security, the CBK ensures that those certified have a consistent and profound understanding of the ever-changing world of cybersecurity. This knowledge is organized into eight distinct information security domains, each offering insights into specific areas of the industry.
Think of it as the CISSP certification syllabus. The CBK provides a comprehensive overview of what is covered in the exam, as well as guidelines in information security, ensuring that certified individuals are well-equipped to address the diverse challenges in today's digital environment.
What are the CISSP domains?
To earn the CISSP certification, you must have a comprehensive understanding of all the 8 domains of cybersecurity. Essentially, these domains act as the foundational pillars for any CISSP aspirant. Let's delve into their specifics.
The first domain of the CISSP certification, making up about 16% of the exam, dives deep into the fundamental aspects of cybersecurity. It focuses on understanding security's inherent nature and honing the skills to assess and manage risk.
Additionally, this CISSP domain highlights the pivotal roles of governance and compliance. It illustrates their integration with security practices and stresses the importance of aligning organizations with existing regulations and standards.
As you journey through this domain, you'll gain insights into the strategic importance of security and risk management, preparing you for the multifaceted challenges of today's cybersecurity landscape. Here is what Domain 1 covers:
- Security governance principles
- Compliance with new and emerging regulations
- Professional ethics in information security
- Business continuity requirements
- Advanced risk management concepts
- Sophisticated threat modeling techniques
- Security policies, standards, procedures, and guidelines
- Security education, training, and awareness
- Incident response and recovery
- Security considerations for emerging technologies
Covering 10% of the CISSP exam, the second domain covers asset security—fundamental to any cybersecurity strategy. At its core, this domain is about safeguarding the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of an organization's assets, whether digital files, databases, or physical infrastructure.
It provides in-depth insights into identifying, classifying, handling, and securing these assets, ensuring protection against unauthorized access, disclosure, changes, or destruction. It equips you with the tools and knowledge to meticulously protect the critical assets that form the backbone of modern enterprises.
Here’s a breakdown of the Domain 2:
- Asset classification and ownership
- Enhanced privacy protection techniques
- Ensuring appropriate asset retention
- Advanced data security controls, including updated encryption methods
- Comprehensive data lifecycle management, including secure disposal methods
- Security principles for cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid assets
- Updated security controls for databases and other storage systems
The third domain, which covers 13% of the CISSP exam, focuses on building a strong foundation for organizational information security. Think of it as building a fortress for data; the walls, moats, and battlements are the technical solutions, protocols, and processes that keep threats at bay.
In this domain, candidates learn how to design, implement, and manage secure systems, with a focus on resistance, detection, and recovery from potential attacks. In addition to understanding various computing platforms and environments, this domain emphasizes the importance of cryptography, a fundamental tool in securing data both in transit and at rest.
Mastering these CISSP topics equips professionals to develop a robust cybersecurity infrastructure, bolstering defenses against the many digital threats out there. Here are other things you can expect from this domain:
- Concepts of secure design principles, incorporating new technologies
- Updated security models fundamental principles
- Security capabilities of information systems, including IoT and mobile devices
- Advanced vulnerabilities and countermeasures in web-based systems and mobile systems
- Expanded cryptography section covering concepts, methodologies, and emerging practices
- Physical security integrated with smart technologies
- Secure protocol and design components, with a focus on new and emerging threats
- Management of the information system lifecycle
The fourth domain, making up 14% of the CISSP exam, focuses on the protection and design of an organization's networks and their communication processes. This domain highlights the importance of secure design, implementation, and control measures to guard against potential eavesdroppers, man-in-the-middle attacks, and other network-based threats.
Given the interconnected nature of our world, expertise in Communication and Network Security is crucial. It ensures that professionals can create, oversee, and protect essential connections integral to our digital existence. Here’s what this domain covers:
- Secure network architecture design for modern infrastructures
- Advanced network defense strategies against sophisticated attacks
- Enhanced security protocols for wireless and mobile networks
- Comprehensive coverage of multilayer protocol security
- Updated encryption methods for secure network communications
The fifth domain, which makes up 13% of the overall CISSP exam, covers all the tools and policies needed to manage, identify, authenticate, and authorize individuals or groups to access system resources. It dives into how organizations can maintain control over access to their systems and data, emphasizing the importance of limiting access to only those who genuinely need it, based on their roles and responsibilities.
Understanding and mastering IAM ensures that candidates can know how to keep data in the right hands, reducing the risk of breaches and unauthorized access, and making it a cornerstone of effective cybersecurity. Below are the topics covered in this domain:
- Advanced identity management lifecycle automation
- Dynamic and risk-based access control models
- Modern federated identity management and SSO technologies
- Expanded use of biometrics and smartcards in authentication
- Comprehensive strategies against identity-related attacks
Accounting for 12% of the CISSP exam, the sixth domain delves into the methodologies and practices behind evaluating, testing, and assessing an organization's security posture. It emphasizes the importance of proactively identifying vulnerabilities, flaws, and weaknesses before they can be exploited by adversaries, ensuring systems are resilient against potential attacks.
By learning the principles of this domain, aspirants can equip themselves with a proactive approach to cybersecurity, continually refining defenses and ensuring systems remain robust in the face of emerging threats. The following topics are included in this domain:
- Advanced assessment, test, and audit strategy design and validation
- Comprehensive security control testing, including AI and ML systems
- Expanded security testing tools and techniques: DAST, SAST, IAST, SCA
- Enhanced data collection and analysis from security processes
- In-depth internal and third-party audit methodologies
- Effective reporting and communication of results with modern tools and visual data representation
The seventh domain of CISSP, which constitutes 13% of the certification exam, dives into the day-to-day tasks and procedures that keep an organization's information assets safe. It emphasizes the need for incident response, disaster recovery, and continuous monitoring to ensure that systems remain secure and resilient against threats, both anticipated and unforeseen.
Candidates who master this domain can ensure the continuous protection of assets, swiftly respond to security events, and adapt defenses based on emerging threats and business needs. Here are the topics covered in this domain:
- Operational security procedures and responsibilities
- Incident response and management
- Disaster recovery (DR) and business continuity (BC) planning
- Data backup and recovery solutions
- Secure logging, monitoring, and audit activities
- Vulnerability management programs
- Physical security components
The CISSP domain 8, which comprises 10% of the CISSP exam, explores the crucial practices and procedures required to ensure that software products remain free of vulnerabilities and flaws that could be exploited by malicious actors. It emphasizes the integration of security throughout the software development lifecycle, from initial design to deployment and maintenance.
With this domain under the candidate’s belt, they can ensure that the very tools and platforms organizations rely on are built with security in mind from the ground up, minimizing risks and maximizing operational integrity. Here are the topics covered in this domain:
- Security integration in the software development lifecycle (SDLC)
- Enhanced security controls in development environments
- Assessments of software security effectiveness
- Advanced secure software deployment practices
- Ongoing software operations and maintenance security
CISSP Overview: What to expect in the CISSP 2024 exam?
Regardless of the language chosen, all candidates will take the exam in the CAT (Computerized Adaptive Testing) format, which consists of 100 to 150 multiple-choice questions and advanced innovative items, to be completed within a 3-hour time limit.
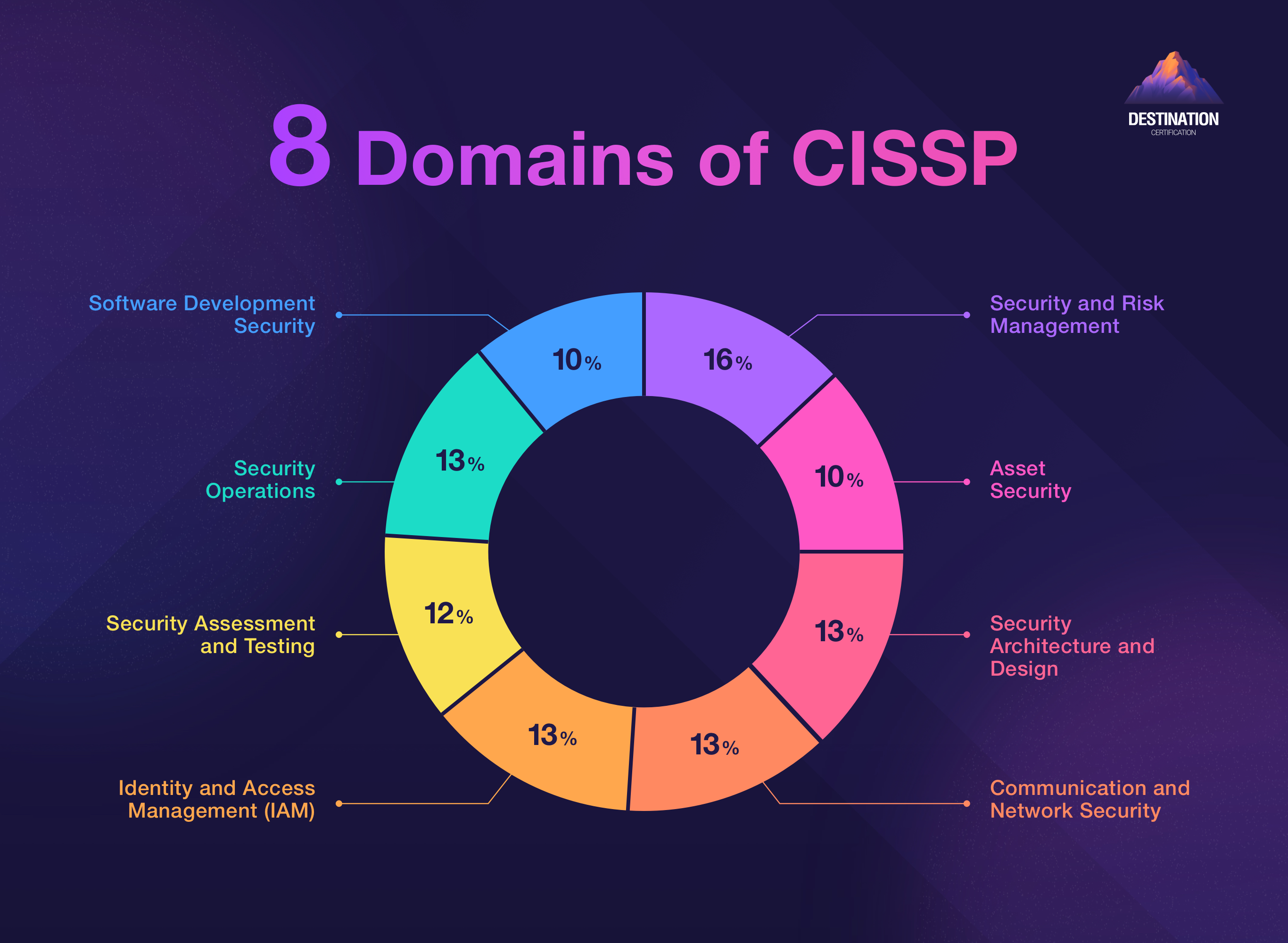
The exam follows the same CISSP domain list and examination weights across all formats. Here are them:
Domains | Average weight |
|---|---|
1. Security and Risk Management | 16% |
2. Asset Security | 13% |
3. Security Architecture and Engineering | 13% |
4. Communication and Network Security | 13% |
5. Identity and Access Management (IAM) | 13% |
6. Security Assessment and Testing | 12% |
7. Security Operations | 13% |
8. Software Development Security | 10% |
Total | 100% |
Go deeper into 8 domains of CISSP
Now that you’re familiar with the CISSP basics, you're equipped to make an informed decision about pursuing this certification. If you're ready to take the plunge, let Destination Certification be your guide.
We've crafted in-depth CISSP domain summaries that dive into each of the ISC2 domains, providing detailed insights into their technical aspects. If you're looking for a deeper exploration of the CISSP topics, our MasterClass is designed to align with your current knowledge and schedule.
In this CISSP online training, the topics discussed are tailored based on your existing familiarity with the CISSP domains, ensuring a comprehensive grasp of all subjects covered in the exam. On top of that, you get a personalized review guide that updates to pinpoint the concepts you still need to reinforce.
The best part? Our courses are led by seasoned CISSP experts with extensive experience in conducting CISSP classes and guiding numerous aspirants to secure their CISSP certification.
So, if you're set on becoming a CISSP, we're here to support you every step of the way.
Rob Witcher
Rob is the driving force behind the success of the Destination Certification CISSP program, leveraging over 15 years of security, privacy, and cloud assurance expertise. As a seasoned leader, he has guided numerous companies through high-profile security breaches and managed the development of multi-year security strategies. With a passion for education, Rob has delivered hundreds of globally acclaimed CCSP, CISSP, and ISACA classes, combining entertaining delivery with profound insights for exam success. You can reach out to Rob on LinkedIn.





