An Overview of Access Control: CISSP Domain 5 MindMap
Download FREE Audio Files of all the MindMaps
and a FREE Printable PDF of all the MindMaps
Your information will remain 100% private. Unsubscribe with 1 click.
Transcript
Introduction
Hey, I’m Rob Witcher from Destination Certification, and I’m here to help YOU pass the CISSP exam. We are going to go through a review of the major topics related to Access Control in Domain 5, to understand how they interrelate, and to guide your studies.
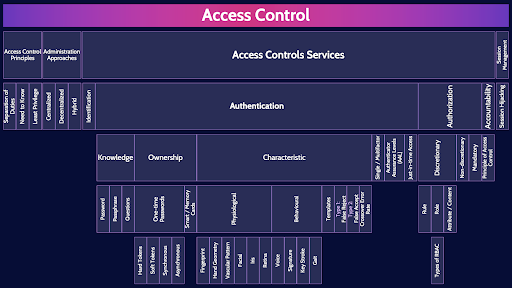
This is the first of two videos for domain 5. I have included links to the other MindMap videos in the description below. These MindMaps are one part of our complete CISSP MasterClass.
Access Control
Access controls are the collection of mechanisms that work together to protect the assets of an organization. These access controls can be both physical controls, like locks, and logical controls, such as a login mechanism to access an operating system.
Access controls enable management to:
- Specify which users
- Can access what resources
- What operations they can perform
- And provide individual accountability
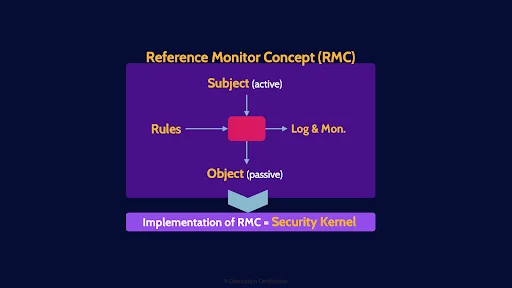
Fundamentally, every access control system is about controlling a subject’s access to an object through some form of mediation, that mediation is based on a set of rules, and all of this is logged and monitored.
This is known as the Reference Monitor Concept.
The implementation of the RMC is known as a security kernel
Thus, every access control system is a security kernel.
Access Control Principles
Now, lets jump into the mind map
There are three major principles that we apply throughout access control
Separation of Duties
The first is Separation of Duties. To divide up key processes into multiple parts assigned to different people.
Need to Know
Need to know and least privilege are very similar - only give users the access they need based on their jon, and nothing more. But there is a subtle difference between them that you need to know. Need to Know is focused on restricting a users KNOWLEDGE (access to data) to only the data required for them to perform their role.
Least Privilege
Whereas, Least Privilege is focused on restricting a users ACTIONS to only those required for them to perform their role.
Administration Approaches
When it comes to administering access to systems (the addition, modification and removal of users) there are three main approaches: centralized, decentralized, and hybrid.
Centralized
In a centralized approach, access to multiple separate applications is managed through one centralized system.
Decentralized
In a decentralized approach, access to multiple applications is managed individually within each application.
Hybrid
Many organizations used a hybrid approach, which is simply some combination of centralized and decentralized.
Access Controls Services
Now let’s talk about the access controls services. There are 4 major services that all access control system must provide: Identification, Authentication, Authorization, and Accountability.
Identification
We’ll start with identification. This is where the user must assert their identity to the system. For example, my username is rwitcher.
Authentication
Authentication is where the system verifies the user’s identity via one of the three factors of authentication: knowledge, ownership, or characteristic
Knowledge
Authentication by knowledge, also referred to as something you know, is where a user verifies their identity by providing some information that they have memorized
Password
It could be a password.
Passphrase
Or a Passphrase. A long sequence of words that are easy to remember
Questions
Or security questions
Ownership
The second factor of Authentication is ownership, also referred to as something you have. Authentication by Ownership are things that we have in our possession
One-time Passwords
The most common form of authentication by ownership is one-time passwords. We call them one-time passwords because they are only meant to be used once.
Hard Tokens

Hard tokens are dedicated pieces of hardware that generate the one-time passwords. Such as an RSA ID key
Soft Tokens
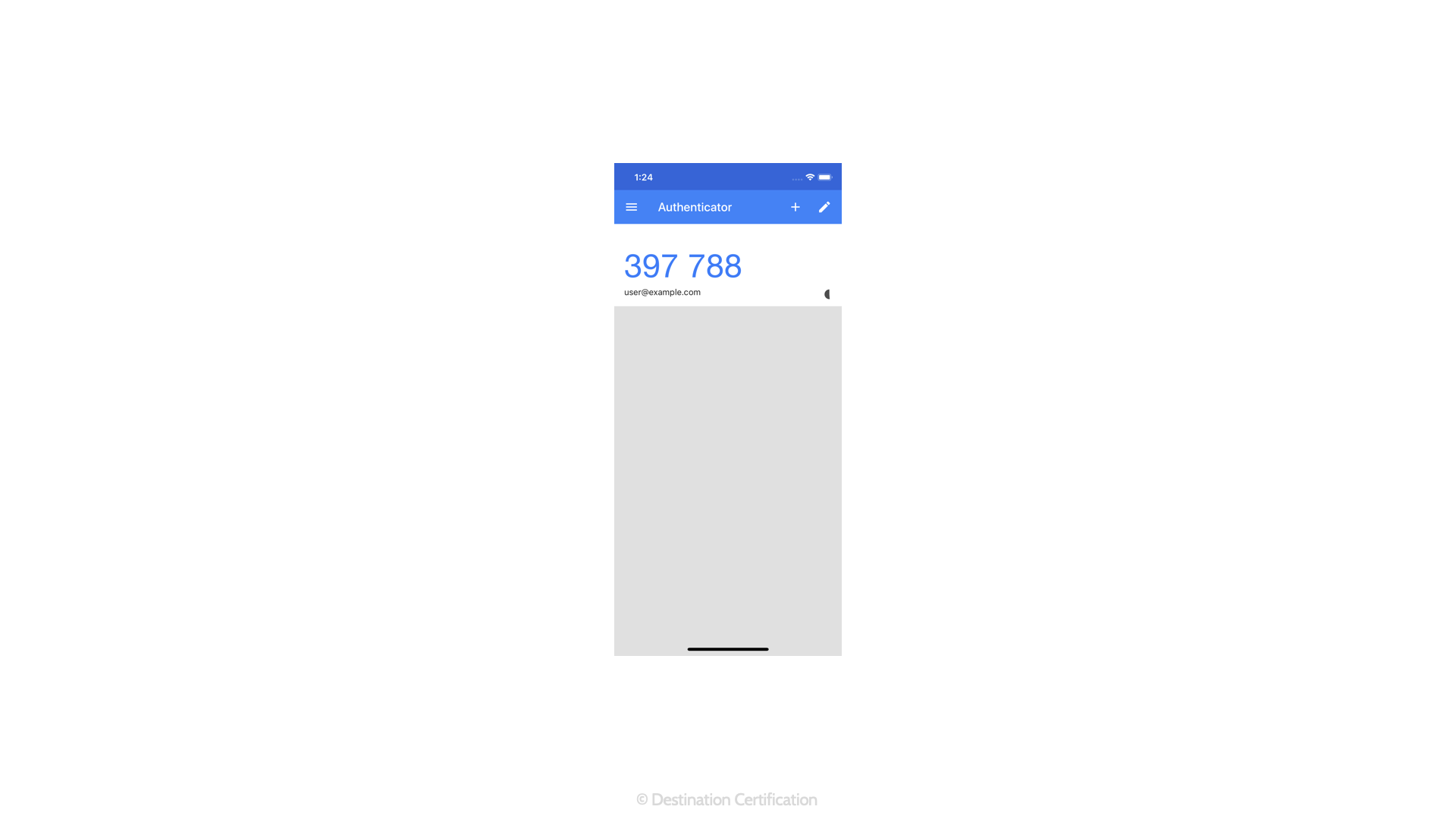
Soft tokens are apps, software, that generate the one-time passwords. Such as the Microsoft or Google authenticator apps that we can install on our mobile phones.
Synchronous
There are two types of hard or soft tokens, Synchronous and Asynchronous.
In a Synchronous system, both the hard or soft token, and the authentication server are generating the same one-time password every 30 to 60 seconds. They are synchronized.
Asynchronous
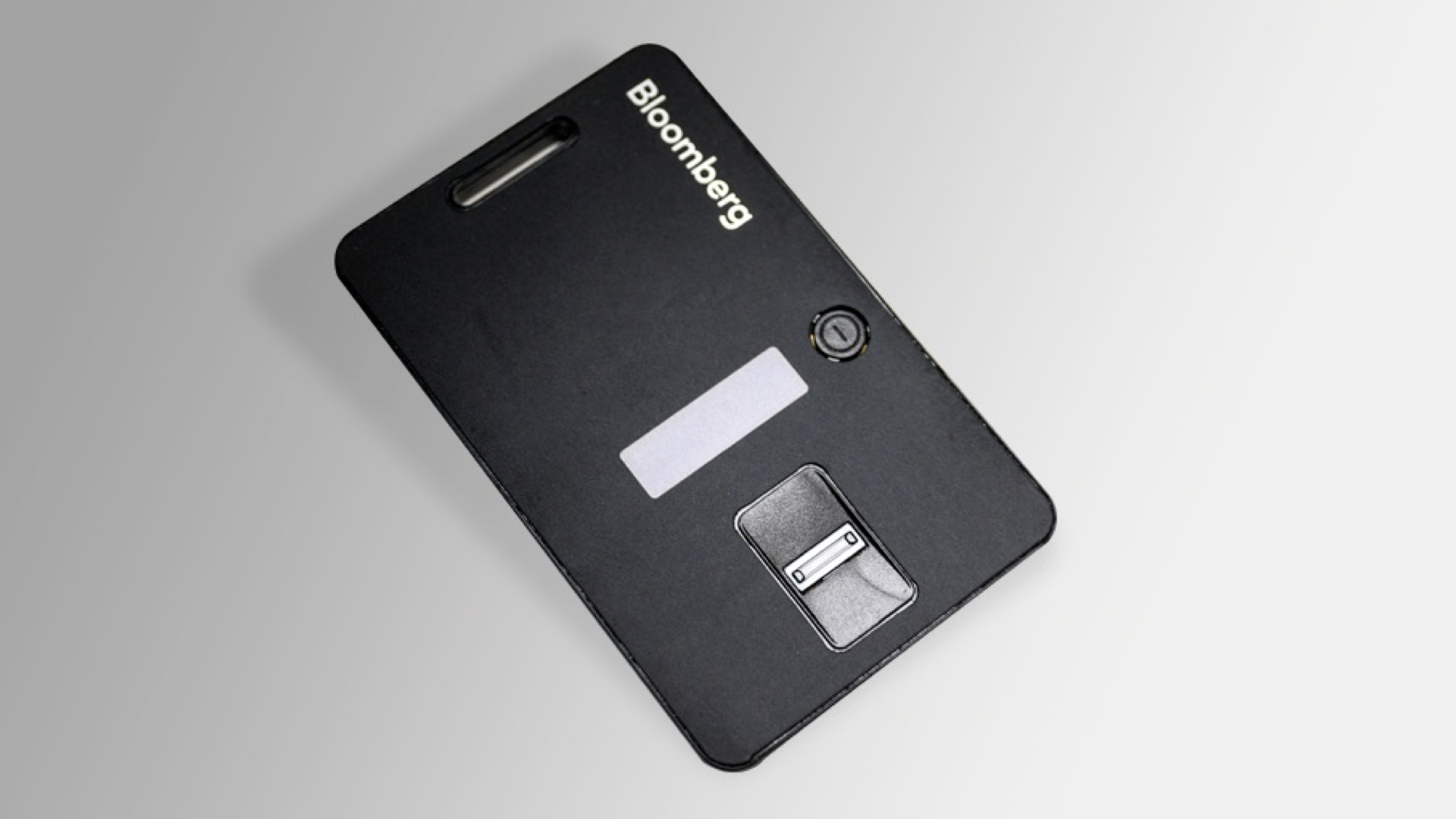

Asynchronous involves a challenge and a response. To authenticate, the user is sent a challenge, which they enter into their hard or soft token device, and a response is generated – the one-time-password. Asynchronous systems are rare, as they are more expensive and complicated, but they are more secure. So in high value situations, like say Bloomberg Financial terminals, they are used.
Smart / Memory Cards
Going back to the other form of authentication by ownership we have Smart cards and memory cards. Smartcards are well named because they have a computer chip within them that provides some smarts. Memory cards on the other hand just store some data that can be read. The same data every time – less secure.
Characteristic
Authentication by characteristic. The reason we call it characteristic and not just biometrics is that there are two main characteristics that we can look at for authentication, physiological and behavioral characteristics.
Physiological
Physiological characteristics are what make up our physiology, our bodies, and are therefore often referred to as biometrics.
Fingerprint
It’s pretty obvious what most of these physiological characteristics are looking at, our fingerprints
Hand Geometry
Hand geometry is looking at the overall dimensions of our hands
Vascular Pattern
Vascular pattern scanners are looking at our vein patterns; often on the back of our hands. When you take the CISSP exam, you are likely to encounter a vascular scanner as many of the pearsonVue testing centers use them as part of registering you to take the exam. They want to make sure that if you step out during the exam to take a break, that it is you coming back into the room and not someone you have hired to write a test for you.
Facial
Facial scanners look at our faces
Iris
Iris scanners look at the coloured ring of our eye. The outside of our eyeball
Retina
Retinal scanners on the other hand look at the vein pattern on the back of our eyeballs. The inside of our eyeball. Retinal scanners are typically considered to be the most accurate of the biometric systems.
Behavioral
Behavioral characteristics are how we act, how we do certain things, like speak, type, and walk
Voice
Voice systems analyze the way we speak, the minutiae of our voices
Signature
Signature systems look at how we write. How we sign our name for example
Key Stroke
Keystroke dynamics systems look at how we type. Characteristics such as dwell and flight time
Gait
And gait dynamics looks at how we walk.
Templates
When a biometric system collects a sample for a user, for example their fingerprint scan, facial scan, etc. the data will be processed to look for unique characteristics and a mathematical representation of the user's unique biometric data will be created. This unique mathematical representation is called a biometric template. Templates can be used in a couple of major ways: in 1 to N (1 to Many) lookup for Identification, and in a 1 to 1 direct comparison for Authentication.
Type 1: False Reject
A challenging aspect of biometric systems for authentication is that they are not binary, and by that I mean they are not 100% sure that it is a valid user and not 100% sure it is an invalid user trying to authenticate. As such we have to deal with two types of errors related to biometric systems. The first is a Type 1: False Reject. This is where a valid user is falsely rejected.
Type 2: False Accept
A type 2: False accept is the inverse. This is where an invalid user, say an attacker, is falsely authenticated and given access. Not Good!
Crossover Error Rate
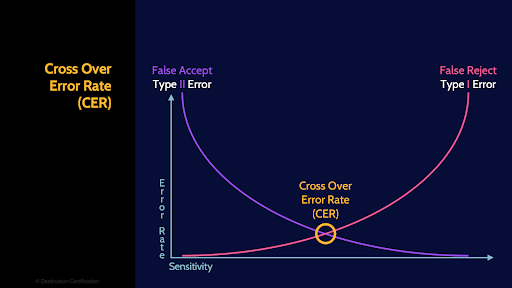
The final piece here related to authentication by characteristic is the CrossOver Error rate. Type 1 and Type 2 errors are inverse to each other. If you graph them, you would see that the line for Type 1 errors will intersect the Line for Type 2 errors, and where they intersect is the aptly named CrossOver Error rate or Equal Error Rate (EER). The Crossover Error Rate is a good measure of the overall accuracy of a biometric system.
Single / Multifactor
We have now discussed the 3 factors of authentication: Knowledge, Ownership and Characteristics. Single Factor authentication is simply one of these factors. Multi-factor authentication means using two or more DIFFERENT factors of authentication.
Authenticator Assurance Levels (AAL)
The Authenticator Assurance Levels is a model for measuring the robustness, the security, of an authentication process. There are 3 levels: AAL 1 is the least secure, and AAL3 is the most secure.
Just-in-time Access
Just-In-Time (JIT) Access is an access control strategy where user access to a system is granted exactly when needed, and only for the duration required to complete a specific task. Essentially, instead of having constant access at all times, users are granted permissions dynamically when they need to use them, and these permissions are revoked once a task is completed. Very cool idea.
Authorization
Now let’s talk about authorization, this is where we define a user’s specific access within a system, what they are authorized to access, and this is where we apply principles like least privilege and need to know.
Discretionary
The first access control philosophy is known as Discretionary Access and the defining characteristic of discretionary access is that the owner of the system is deciding who is authorized to access what. This is a very good security practice as owners best understand their systems, and are accountable for the security of their systems.
Rule
Within discretionary access we have Rule based, just a list of rules in a file, or an ACL, access control list
Role
Role based access, where we create roles, define the access for those roles, and then assign one or more roles to a user. The roles assigned to a user define a user’s access.
Types of RBAC
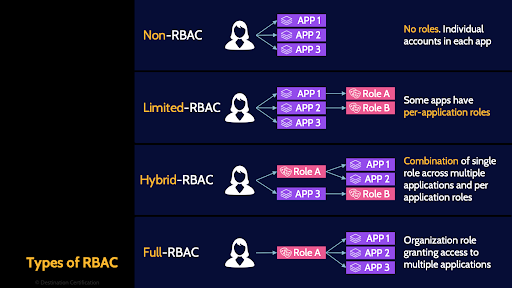
There are four major types of RBAC that you should be familiar with.
Non-RBAC means there is no roles based access.
Limited-RBAC means within specific applications you can create roles and the role within an application will only define a user’s access in that specific application
Hybrd-RBAC is where you get to the point where you can create role, and through that role you can define a user’s access in multiple different applications. But not every application across the organization is integrated into the role based access system
Which brings us to Full-RBAC. Full-RBAC means through a role you could grant a user access to any application across the organization. Most companies don’t get to Full-RBAC and instead use Limited or Hybrid-RBAC.
Attribute / Context
And attribute-based access, sometimes referred to as context based. Where we look at a series of different attributes to make an authorization decision: source IP address, geo location, OS type, classification of asset being accessed, etc.
Non-discretionary
The next access control philosophy is known as Non-Discretionary. Discretionary means the owner decides. So non-discretionary means someone other than the owner decides who is authorized to access what – like an IT helpdesk person. This is not a good security practice.
Mandatory
The last and final access control philosophy is known as Mandatory. Mandatory means the system decides. Based on the security clearance of users and the classification of assets. Labeling is an important requirement for Mandatory access.
Accountability
The final and most important access control service is Accountability. To have security, we must ensure users are accountable for their actions on a system.
Principle of Access Control
Because accountability is the most important access control service, we give it a special name: the principle of Access Control. So, remember, the principle of access control is accountability and accountability is the principle of access control.
Session Management
The Final piece here is session management. Whenever a user has identified themselves, been authenticated and authorized into a system, this begins a session. Session management is all about managing these sessions to ensure they are secure.
Session Hijacking
The major risk we are concerned with related to sessions is session hijacking.

And that is an overview of Access Control within Domain 5, covering the most critical concepts you need to know for the exam.
As you’re no doubt seeing as you go through these MindMap videos, there is an immense amount of information across a huge number of topics that you need to know to pass the CISSP exam.
A huge challenge most people like yourself face is figuring out what they need to focus on. What exactly do you already know, and what do you need to focus on in your studies.
This is a problem that we have solved for our students. Our CISSP MasterClass will automatically build an extremely detailed personalized guide for you that will show you exactly what you need to focus on in your studies, and even better, all of the extensive super high-quality study materials we have built are instantly accessible to you.
We show you exactly what you need to study and provide all the study materials you need to confidently pass the CISSP exam.
You can learn more about our CISSP MasterClass here: destcert.com/CISSP
Link in the description below as well.

If you found this video helpful you can hit the thumbs up button and if you want to be notified when we release additional videos in this MindMap series, then please subscribe and hit the bell icon to get notifications.
I will provide links to the other MindMap videos in the description below.
Thanks very much for watching! And all the best in your studies!
